Anti-rat NIS (affinity purified)
| Volume | 100 µl |
| Concentration | 1mg/mL |
| Antigen | Synthetic peptide corresponding to residues 603-618 of the rat sodium iodide symporter (rNIS) |
| Species | Rabbit |
| Reactivity | Rat, Mouse |
| Isotype | IgG |
-
Description
Our anti-rat NIS antibody is a polyclonal affinity purified antibody that detects both the native and denatured forms of the rat sodium iodide symporter (rNIS). This antibody recognizes an intracellular C-terminal epitope that is conserved between rat and mouse NIS.
Immunofluorescence staining for rat NIS expression
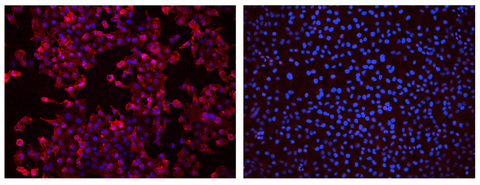
Tissue: HelaH1 cells stably-expressing (left) rat NIS or (right) human NIS were permeabilized
Type: Cytospin of cells on glass slide
Stain: Anti-rat NIS antibody followed by an Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated anti-rabbit secondary antibody and Hoechst 33342 to stain nuclei. Cell photos were taken at 200X magnification.
Dilution: 1:500
Recommended Dilution: 1:500
Immunoblotting for rat NIS protein
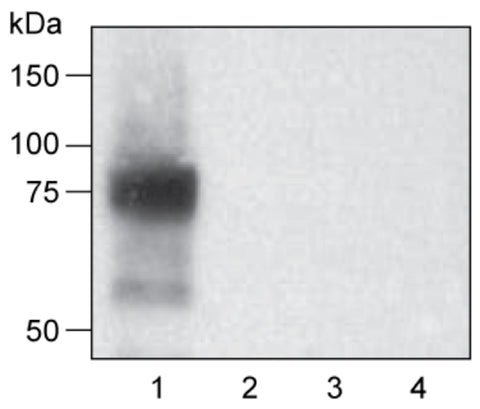 Recommended Dilution: 1:1000-1:5000
Recommended Dilution: 1:1000-1:5000Total protein (10 mg) from HeLaH1 cells stably-expressing rat (lane 1), dog (lane 2), pig (lane 3), or rhesus (lane 4) NIS were subjected to SDS-PAGE and western blot analysis using anti-rat NIS antibody (1:3,000 dilution) and HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit secondary antibody. The top band (~75-90 kDa) represents the hyperglycosylated form of rNIS, while the bottom band (~60 kDa) represents the hypoglycosylated form of rNIS. Data from Dr. Nancy Carrasco’s (Yale University) laboratory.
For immunoblotting of NIS proteins, it is recommended that samples be heated at 37°C for 30 minutes prior to loading for SDS-PAGE (do not boil).
Flow Cytometry
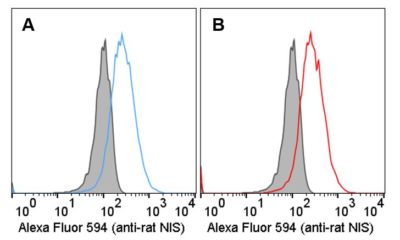 Tissue: (A) HelaH1 cells stably-expressing rat NIS (blue) or parental HelaH1 cells (grey) were fixed with paraformaldehyde and permeabilized
Tissue: (A) HelaH1 cells stably-expressing rat NIS (blue) or parental HelaH1 cells (grey) were fixed with paraformaldehyde and permeabilizedType: Versenized cells
Stain: Anti-rat NIS antibody followed by an Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated anti-rabbit secondary antibody
Dilution: 1:500
-
Citations
Product Citations
Levy et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1997. 94:5568-5573
De la Vieja et al. J. Cell Sci. 2004. 117:677-687
Nicola et al. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009. 296:C654-C662
Tazebay et al. Nat. Med. 2000. 6:871-878
Paroder-Belenitsky et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011. 108:17933-38.
-
Datasheet/COA
Lot Number REA-IM09