CT26.WT-mNIS-Neo/eGFP-Puro
| Species | Mouse |
| Cell Type | Colorectal Carcinoma |
| Transgene | Mouse sodium iodide symporter (mNIS) Enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) |
| Selection Genes | Neomycin (Neo) Puromycin (Puro) resistance |
-
Description
CT26.WT-mNIS-Neo/eGFP-Puro is a polyclonal population of the mouse colorectal carcinoma cell line CT26.WT (ATCC® CRL-2638™). To achieve stable reporter expression in the polyclonal population, parental CT26.WT cells were transduced with LV-mNIS-P2A-Neo (LV025) and LV-eGFP-PGK-Puro (LV031) and selected using G418 and puromycin. LV-mNIS-P2A-Neo (LV025) expresses the mouse sodium iodide symporter (mNIS) cDNA linked to the neomycin resistance gene (Neo) via a P2A self-cleavage peptide under the spleen focus-forming virus (SFFV) promoter. LV-eGFP-PGK-Puro expresses enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) cDNA under the SFFV promoter and the puromycin resistance gene under the phosphoglycerate kinase promoter (PGK).
*The ATCC trademark and trade name and any and all ATCC catalog numbers are trademarks of the American Type Culture Collection.
This cell line has been tested for mycoplasma contamination and is certified mycoplasma free.
The parental CT26.WT cell line has been authenticated and certified free of interspecies cross contamination by short tandem repeat (STR) profiling with 9 STR loci.
Due to the immunogenicity of the reporter genes in this cell line, we recommend using immunocompromised mice for in vivo studies.
-
Characterization
Morphology
 Low and high density cell morphology (200x)
Low and high density cell morphology (200x)NIS Expression
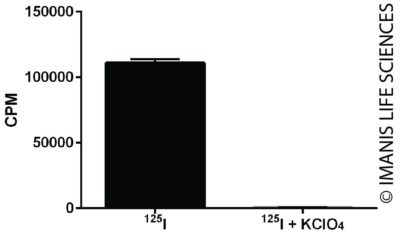 Cells were incubated with I-125 for one hour in the presence or absence of KClO4, an inhibitor of iodine uptake. Radioiodine concentrated within the cells was measured with a gamma counter.
Cells were incubated with I-125 for one hour in the presence or absence of KClO4, an inhibitor of iodine uptake. Radioiodine concentrated within the cells was measured with a gamma counter.eGFP Expression
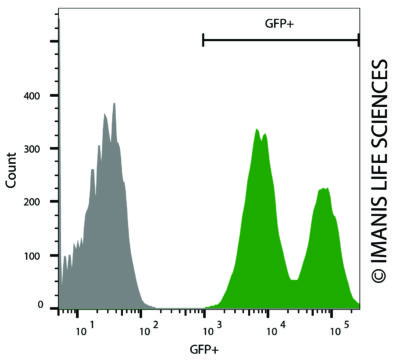 Flow cytometry of CT26.WT-mNIS-Neo/GFP-Puro (green) and control (gray) cells.
Flow cytometry of CT26.WT-mNIS-Neo/GFP-Puro (green) and control (gray) cells. -
Growth Conditions
Complete Growth Medium: DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 1X Penicillin/Streptomycin, 3 µg/mL puromycin, and 0.4 mg/mL G418.
The addition of puromycin and G418 to the complete growth medium maintains high reporter expression over continued passage of the cells. It is highly recommended, especially if the cells undergo multiple passages prior to being used for studies.
These cells should be grown in the indicated medium and passaged when they reach confluency. For routine passaging, cells are recommended to be split at a 1:10 ratio every 3-4 days.
CT26.WT cells easily detach from tissue culture surfaces. Coating culture plates with poly-D-Lysine prior to use is recommended for applications involving frequent washes, culture media changes, or rocking.
-
Usage Information
These cells are suitable for in vitro and in vivo experimentation. CT26.WT cells form tumors and pulmonary metastases post implantation into syngenic Balb/c mice.1 The NIS transgene facilitates high resolution, 3D SPECT/PET imaging of implanted cells. NIS is not immunogenic and is therefore suitable for longitudinal imaging studies in a syngenic model.
The cells can be amplified in vitro and used to generate additional frozen stocks. Cryopreservation of low passage stocks is recommended. Frozen stocks should be preserved in a designated cryopreservation medium.
These cells were generated via lentiviral vector transduction. The lentiviral vector used for transduction was a self-inactivating (SIN) vector in which the viral enhancer and promoter have been deleted. Transcription inactivation of the LTR in the SIN provirus increases biosafety by preventing mobilization by replication competent viruses and enables regulated expression of the genes from the internal promoters without cis-acting effects of the LTR2. Nevertheless, all work with these cells should be performed under biosafety-level 2 (BSL2) conditions by trained personnel. Institutional requirements may permit handling of these cells under BSL1 conditions if certain criteria are met.
References:
1Wang et al. J Immunol. 1995. 154:4685-4692.
2Miyoshi et al. J Virol 1998. 72:8150-8157. -
Datasheet/COA
Lot Number CL-IM50